



Add a personal touch! Gift orders include a handwritten note with your message on a beautifully customized postcard, making each bottle even more special.




Add a personal touch! Gift orders include a handwritten note with your message on a beautifully customized postcard, making each bottle even more special.
Extra virgin olive oil has long been revered as a staple of the Mediterranean diet, praised not only for its flavor but for the multitude of health benefits it offers. From its high concentration of monounsaturated fatty acids to its anti-inflammatory properties, the health benefits of olive oil are numerous and well-documented. These properties contribute significantly to reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, making it a key component in promoting heart health. This article explores the science-backed advantages of olive oil consumption, showing why this liquid gold is a cornerstone of good health.
The use of olive oil dates back thousands of years, with the Ancient Greeks valuing it not only as a food but also for its cultural and medicinal significance.
Extra virgin olive oil stands apart from other types of olive oil due to its rigorous extraction process. The olives, harvested from the olive tree (Olea europaea), are carefully chosen, and mechanical methods are used to preserve the oil’s natural composition. This ensures that extra virgin olive oil contains higher levels of antioxidants and phenolic compounds, which contribute to its health benefits through their antioxidant activities. As a result, EVOO is often recommended by health professionals as the most beneficial form of olive oil.
Not only does the process maintain the natural flavor of the olive oil, but it also ensures that the oil remains rich in healthy fats like monounsaturated fatty acids. These fats are crucial for many health benefits of extra virgin olive oil, from heart health to cognitive function. As more people become aware of the advantages of olive oil consumption, extra virgin olive oil continues to rise in popularity due to its unparalleled quality and health benefits.


Healthy fats are a cornerstone of a balanced diet, providing essential energy, supporting the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and playing a vital role in maintaining heart and brain health. Among the different types of dietary fats, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) are especially prized for their positive impact on human health. Extra virgin olive oil is one of the richest natural sources of MUFAs, particularly oleic acid, which has been linked to a wide range of health benefits.
Regular olive oil consumption, especially as part of the Mediterranean diet, has been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, certain cancers, and other chronic diseases. The Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes extra virgin olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish, is renowned for its ability to improve cholesterol levels, lower blood pressure, and promote overall cardiovascular health. By choosing healthy fats like those found in virgin olive oil over saturated fats and processed oils, you can support your body’s long-term well-being and reduce the risk of developing chronic health conditions. Incorporating extra virgin olive oil into your daily routine is a delicious and effective way to harness the power of healthy fats for optimal health.
Extra virgin olive oil is the highest quality olive oil available, extracted from olives using a cold press method that ensures no chemical treatment or heat processing. This method avoids high temperatures, which can degrade important nutrients and antioxidants in olive oil. As a result, extra virgin olive oil retains the maximum amount of nutrients and antioxidant properties, making it more potent in terms of health benefits.
Olive oil is a nutrient-rich powerhouse that offers a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The type of fat in olive oil is primarily monounsaturated, with oleic acid being the most abundant. This healthy fat is known for its heart-protective properties and ability to reduce inflammation.
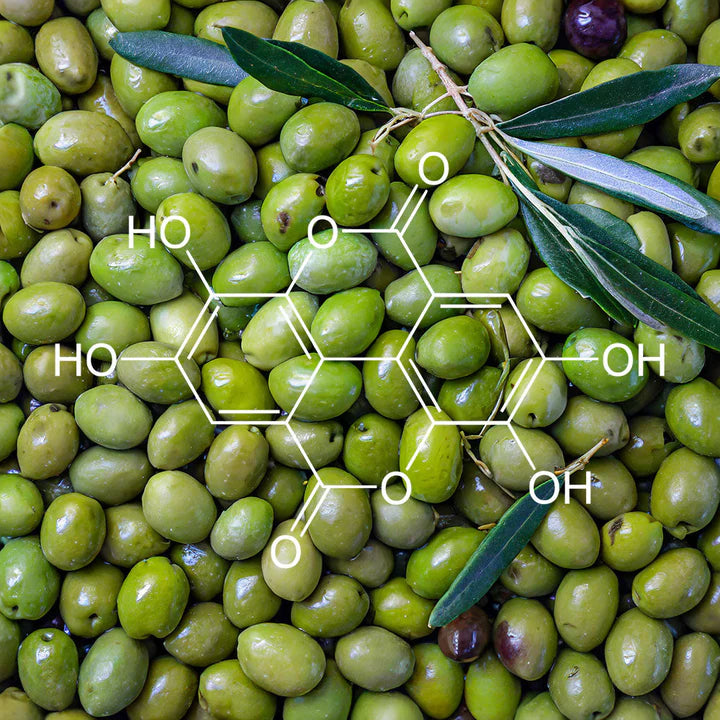
In addition to its healthy fats, olive oil is a rich source of antioxidants, including vitamin E, polyphenols, and other antioxidants. Among these, polyphenols—specifically plant polyphenols—are recognized for their potent health-promoting properties. These polyphenols are part of the broader group of phenolic components, which are key bioactive compounds with antioxidant, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects. These antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting the body against oxidative stress, which can lead to chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. The combination of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants makes olive oil a valuable addition to any diet, offering numerous health benefits.
Extra virgin olive oil is an excellent source of monounsaturated fatty acids, particularly oleic acid. These healthy fats account for up to 73% of the total fat content in olive oil. Consuming foods rich in monounsaturated fats has been shown to improve heart health by improving cholesterol levels. Olive oil consumption can also positively influence the overall lipid profile, helping to balance triglycerides, total cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol.
The monounsaturated fatty acids found in extra virgin olive oil are well known for their heart-protective properties. The primary monounsaturated fat in olive oil is oleic acid, which has been studied extensively for its ability to reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Diets rich in olive oil, especially extra virgin olive oil, have been linked to lower rates of cardiovascular diseases, a testament to the profound health benefits of extra virgin olive oil. Olive oil has also been shown to help lower low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and prevent LDL oxidation, further reducing the risk of heart disease. The combination of olive oil and fish oil can be particularly effective in controlling inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing the importance of including both oils in the diet for optimal health benefits.
In addition to heart health, monounsatured fatty acids support metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity, making olive oil a valuable asset in managing blood sugar levels. Consuming olive oil regularly ensures that you are getting a healthy dose of these beneficial fats, which are essential for overall well-being. The Mediterranean diet exemplifies how these fats can contribute to a longer, healthier life.

One of the key components in extra virgin olive oil is oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid that provides several cardiovascular benefits. Studies suggest that oleic acid can help reduce inflammation, lower blood pressure, and protect against heart disease, including significantly lowering the risk of coronary heart disease, making it one of the most significant health benefits of olive oil.
Oleic acid is not only responsible for the distinct flavor of extra virgin olive oil but also plays a pivotal role in providing many of the oil’s health benefits. This monounsaturated fatty acid has been shown to reduce blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, it can improve endothelial function, allowing blood vessels to dilate properly, enhancing circulation and reducing the risk of heart-related complications.
Studies also indicate that oleic acid may have cancer-fighting properties. By inhibiting certain cancer cell pathways, it may help reduce the risk of cancer development. Extra virgin olive oil provides a substantial amount of oleic acid, making it a powerful tool for those seeking to enhance their overall health and protect against chronic illnesses.
Research shows that consistently consuming olive oil can lower the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. The Mediterranean diet, which is high in olive oil, has been associated with a reduced risk of these diseases due to its fats, including monounsaturated fatty acids. Olive oil is a source of heart healthy fats, which are known to support cardiovascular health.
High olive oil consumption, particularly of extra virgin olive oil, has been consistently associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Choosing olive oil, which is low in saturated fat compared to other oils, provides additional benefits for heart health. The antioxidants in olive oil, such as polyphenols, play a critical role in reducing oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory properties of olive oil further contribute to protecting the heart.
The benefits of extra virgin olive oil extend to improving cholesterol levels. This balancing effect is key in maintaining healthy arteries and preventing the buildup of plaque, which can lead to strokes or heart attacks. The Mediterranean diet is one of the best-documented diets for promoting heart health and reducing mortality from cardiovascular diseases.
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes eating whole foods and straying away from processed foods. In this diet, extra virgin olive oil is the primary fat source. Numerous studies have highlighted the role of the Mediterranean diet in promoting longevity and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, thanks in large part to the health benefits of extra virgin olive oil.
The Mediterranean diet is more than just a way of eating; it’s a lifestyle that promotes longevity and well-being. One of the cornerstones of this diet is the daily consumption of olive oil, particularly extra virgin olive oil. Studies have shown that individuals who follow the Mediterranean diet tend to have lower risks of heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases, thanks in large part to the health benefits of olive oil. Additionally, research suggests that the Mediterranean diet may also help protect against other diseases, such as liver diseases, kidney toxicity, and inflammation, due to the beneficial components found in olive oil.
The inclusion of olive oil in nearly every meal provides an abundance of healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated fatty acids and oleic acid, which are essential for overall health. The Mediterranean diet’s high intake of meat and fish, vegetables, fruits, and olive oil, ensures that the body receives a wide variety of nutrients, all contributing to better health outcomes. This dietary pattern is not only beneficial for physical health but also supports mental well-being and cognitive function.


Chronic inflammation is a leading driver of many diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Extra virgin olive oil contains bioactive compounds such as oleocanthal and oleuropein, which have potent anti inflammatory effects. These compounds work similarly to non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in reducing inflammation, further highlighting the anti inflammatory benefits of extra virgin olive oil.
The anti-inflammatory benefits of olive oil are among the most significant factors in its health-promoting properties. Oleocanthal, a powerful compound found in extra virgin olive oil, mimics the effects of ibuprofen, making olive oil a natural anti-inflammatory food. This is particularly important for those suffering from chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome, where olive oil can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Additionally, olive oil's anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, largely attributed to its plant polyphenols and monounsaturated fatty acids like oleic acid, may offer benefits in the prevention and management of autoimmune diseases by modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation associated with these conditions.
Regular intake of extra virgin olive oil, particularly as part of the Mediterranean diet, has been associated with lower levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). These anti-inflammatory effects make olive oil a vital component of a diet aimed at preventing chronic diseases. By reducing inflammation, olive oil helps maintain the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes in the body, promoting better overall health.
Beyond its well-known cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory benefits, olive oil also boasts impressive antimicrobial properties. The polyphenols found in olive oil, particularly hydroxytyrosol, have demonstrated the ability to combat a variety of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This natural antimicrobial activity makes olive oil a valuable ally in protecting the body against infections, especially those affecting the respiratory and digestive systems.
The antimicrobial effects of olive oil may also enhance its anti-inflammatory benefits, as many chronic inflammatory conditions are linked to underlying microbial imbalances or infections. By incorporating olive oil into your diet—whether as a cooking oil, salad dressing, or dietary supplement—you may help support your body’s defenses against common pathogens. These additional health benefits of olive oil further underscore its role as a functional food that not only supports cardiovascular health but also contributes to overall immune resilience and well-being.
Olive oil’s high concentration of antioxidants and monounsaturated fats can also have neuroprotective effects. These benefits are closely linked to olive oil's positive impact on the central nervous system, where its polyphenols and healthy fats help modulate neuroinflammation and support brain health. The monounsaturated fatty acids in olive oil have been linked to improved brain function and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. In the Mediterranean diet, high olive oil intake is often associated with a lower incidence of neurodegenerative diseases.
Research continues to show that the monounsaturated fats in olive oil, particularly oleic acid, are not only beneficial for heart health but also for brain health. Diets rich in olive oil have been linked to a lower risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s. The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in extra virgin olive oil help protect the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in the aging process. The health effects of olive oil, including its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, contribute significantly to maintaining brain health and reducing the risk of neurological disorders. This 28-year study found that people who took in more than 7 grams of olive oil per day (about half a tablespoon or more) had a 28% lower risk of dementia-related death, regardless of their diet quality, compared with people who never or rarely had olive oil.
Moreover, studies suggest that olive oil consumption may enhance learning and memory function. Incorporating olive oils into a balanced diet provides the brain with the necessary fats to support cognitive performance, especially in older adults. The Mediterranean diet, with its heavy reliance on olive oil, has been shown to protect against mental decline and foster overall mental well-being.
Extra virgin olive oil is packed with powerful antioxidants like Vitamin E and polyphenols, which help protect the body against oxidative stress, a key factor in aging and the development of chronic diseases. The antioxidants in olive oils can neutralize harmful free radicals, helping to prevent cell damage.
The antioxidant content of extra virgin olive oil is one of its most compelling health benefits. These antioxidants, including vitamin E and phenolic compounds, neutralize free radicals in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, leading to chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. The results of consuming olive oil in this context are profound, as it acts as a natural shield against these damaging molecules.
Beyond its antioxidant power, olive oil also plays a role in promoting the health of various systems in the body, such as the immune and cardiovascular systems. The combination of antioxidants and fats in olive oils supports cellular health, reduces inflammation, and helps maintain the integrity of cell membranes. This makes olive oil not just a cooking ingredient but a potent health-enhancing food that can have a profound effect on long-term wellness.


There is growing evidence that olive oil can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for people with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. Olive oil's healthy fats and antioxidant properties help improve insulin resistance, allowing for better glucose regulation.
The healthy fats in extra virgin olive oil, particularly monounsaturated fatty acids, improve insulin sensitivity, which is critical for blood sugar regulation. For individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk, olive oil can significantly improve glycemic control, reducing blood sugar spikes after meals. This makes olive oil an excellent addition to any diet aimed at managing diabetes or pre-diabetes conditions.
Moreover, the polyphenols found in olive oil have been shown to reduce the risk of insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. By incorporating olive oils into your meals, especially extra virgin olive oil, you not only enjoy better blood sugar control but also a lower risk of developing metabolic disorders. The Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil, is a well-documented approach to improving metabolic health and preventing the onset of diabetes.
Another advantage of olive oil consumption is its positive effect on digestive health. Olive oil has a mild laxative effect and can help prevent constipation. Moreover, it promotes a healthy gut microbiome, supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines.
Olive oil’s benefits extend beyond the cardiovascular and metabolic systems; it also supports digestive health. The healthy fats in extra virgin olive oil promote the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, which are essential for gut health. Furthermore, olive oil’s natural laxative properties help to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements.
Additionally, recent research has shown that olive oil can have a positive impact on the gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract. Olive oil contains phenolic compounds that act as prebiotics, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall health, as it influences everything from digestion to immune function. By including extra virgin olive oil in your diet, you help maintain a balanced and healthy digestive system. Notably, some studies suggest that olive oil’s beneficial effects on gut health may also contribute to a reduced risk of colorectal cancer, due to its anti-inflammatory properties and influence on gut bacteria.
Click on this article to learn more about olive oil and gut health.
Despite being calorie-dense, olive oil can support weight management. Studies have shown that diets rich in olive oils are linked to lower body weight and fat mass. In particular, olive oil consumption has been associated with a reduction in body fat, supporting improvements in overall body composition. Olive oil enhances satiety, meaning you feel fuller for longer, which can help in reducing overall calorie intake.
While olive oil is calorie-dense, it has been shown to help with weight gain due to its ability to enhance satiety. The healthy fats in olive oil, particularly monounsaturated fatty acids, help you feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking between meals. This is one of the key olive oil benefits, particularly for those looking to maintain or lose weight without sacrificing nutrition.
Moreover, studies have shown that individuals who follow a diet high in olive oil, such as the Mediterranean diet, tend to have lower body mass indexes (BMIs) and better body composition. This suggests that consuming olive oil, despite its calorie content, can support healthy weight management over time. By incorporating olive oils into a balanced diet, you can achieve better portion control and a more satisfying eating experience.

The antioxidants and healthy fats in extra virgin olive oil also extend to skin health. Olive oil can be applied topically or consumed to promote a youthful appearance by reducing wrinkles and improving skin elasticity. The vitamin E content in olive oil helps protect the skin from sun damage and oxidative stress.
Olive oil has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for skin health. Its high antioxidant content, particularly vitamin E, helps protect the skin from oxidative stress caused by free radicals, which contribute to aging and skin damage. When applied topically, extra virgin olive oil can moisturize the skin, reduce inflammation, and promote wound healing.
Internally, the healthy fats in olive oil help nourish the skin from the inside out. Regular olive oil consumption has been linked to improved skin elasticity and reduced appearance of wrinkles. Olive oils can also help protect the skin from UV damage, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage. By integrating olive oil into your daily routine, both through consumption and topical application, you can maintain healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
Several studies suggest that the antioxidants and healthy fats in olive oil may have cancer prevention properties. The polyphenols found in olive oil, along with its high oleic acid content, have been shown to reduce cancer risk for certain types of cancers. These compounds work by inhibiting the proliferation of cancer cells and promoting their death.
The antioxidants in extra virgin olive oil, particularly polyphenols, play a significant role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer. These antioxidants protect cells from oxidative stress, which can lead to mutations and the development of cancer cells. Additionally, oleic acid, the primary monounsaturated fat in olive oil, has been shown to inhibit the expression of genes that are associated with cancer growth.
Epidemiological studies suggest that populations with high olive oil consumption, such as those following the Mediterranean diet, tend to have lower incidences of certain cancers, particularly colon cancer and breast cancer. The potential of olive oil in cancer prevention is attributed to its anti-inflammatory properties and its ability to improve cellular health. Including extra virgin olive oil as part of a balanced diet may provide a protective effect against cancer.
Olive oil has been shown to have a positive effect on bone health, particularly in older adults. The high levels of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants in olive oil may help to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. A study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that women who consumed a Mediterranean-style diet rich in olive oil had higher bone density and a lower risk of osteoporosis compared to those who consumed a low-fat diet.
The antioxidants in olive oil, such as polyphenols, help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which can contribute to bone loss. By incorporating extra virgin olive oil into your diet, you can support bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet, especially for older adults.


The high antioxidant content of extra virgin olive oil can help slow down the aging process by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Regular consumption of olive oil can help protect your cells, tissues, and organs from age-related damage, promoting longevity and overall wellness.
The high concentration of antioxidants in extra virgin olive oil makes it a powerful tool in combating the signs of aging. These antioxidants, particularly polyphenols, help neutralize free radicals that contribute to the aging process. By reducing oxidative stress, olive oil helps protect cells and tissues from damage, promoting longevity and slowing down the aging process.
The anti-inflammatory properties of olive oil further contribute to its anti-aging benefits. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of age-related diseases, and by reducing inflammation, olive oil can help prevent conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive decline. Whether applied topically or consumed as part of the diet, the results of olive oil for anti-aging are clear, making it a valuable addition to any longevity-focused regimen.
Olive oil also plays a role in enhancing immune function. The polyphenols in olive oils have been shown to strengthen the immune system, helping to defend the body against infections and diseases. Consuming olive oil regularly can support your immune support, particularly as you age.
The polyphenols found in extra virgin olive oil are not only antioxidants but also immune-boosting compounds. These bioactive compounds help modulate the immune response, promoting a balanced and healthy immune system. Olive oil has been linked to enhanced immune function, particularly in older adults who are more vulnerable to infections and immune-related diseases.
Moreover, the anti-inflammatory effects of olive oils support immune health by reducing chronic inflammation, which can weaken the immune system over time. Regular consumption of olive oil, especially extra virgin olive oil, ensures that your body receives a steady supply of these immune-supporting compounds, helping to protect against illnesses and maintain overall health.
Olive oil has been shown to have a positive effect on mental health, particularly in reducing the risk of depression and anxiety. The high levels of monounsaturated fats and antioxidants in olive oil may help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to mental health disorders. A study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders found that individuals who consumed a Mediterranean-style diet rich in olive oil had a lower risk of depression compared to those who consumed a low-fat diet.
Additionally, the antioxidants in olive oil may help to improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline. By incorporating extra virgin olive oil into your diet, you can support not only your physical health but also your mental well-being, making it a key component of a holistic approach to health.


Incorporating extra virgin olive oil into your diet can significantly reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. The healthy fats in olive oil help improve insulin resistance, leading to better blood sugar control. Regularly consuming olive oil can lower the chances of developing diabetes by up to 40%.
One of the most significant benefits of olive oil is its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, making it an essential food for those looking to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes. Olive oil's monounsaturated fats help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing insulin resistance, which is a major risk factor for diabetes. Incorporating extra virgin olive oil into meals has been shown to reduce blood sugar spikes, leading to more stable glucose levels.
Moreover, the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in olive oil, has been extensively studied for its protective effects against diabetes. Research shows that individuals who follow this diet have a significantly lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those who follow Western diets high in processed foods and processed fats. Adding olive oil to your diet is thus a simple and effective way to improve metabolic health and prevent diabetes.
Extra virgin olive oil is increasingly recognized for its therapeutic potential in the prevention and management of a variety of health conditions. Thanks to its high content of oleic acid and other beneficial compounds, virgin olive oil has been studied for its role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, colon cancer, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. The anti-inflammatory properties of extra virgin olive oil are particularly noteworthy, with research showing effects comparable to those of ibuprofen, making it a natural option for alleviating symptoms of inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, the antioxidant properties of extra virgin olive oil help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress, a key factor in the development of chronic diseases. The combination of these beneficial compounds makes extra virgin olive oil a powerful tool for supporting human health and reducing the risk of conditions such as colon cancer and metabolic syndrome. As research continues to uncover new therapeutic applications, it’s clear that regular inclusion of extra virgin olive oil in the diet offers far-reaching health benefits that go well beyond basic nutrition.
Incorporating olive oil into your diet can be easy and delicious. Here are some tips for using olive oil in your cooking:
Unlike many seed oils, which have been linked to negative health impacts, olive oil is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. When used appropriately in the diet, olive oil does not have the harmful effect associated with some other oils or fats.


To fully enjoy the health benefits of olive oil, it's crucial to select a high-quality variety, specifically extra virgin olive oil vs. other oils. This is because only the best olive oils, like EVOO, retain the highest levels of antioxidants, healthy fats, and phenolic compounds due to their minimal processing. Unlike refined and regular olive oil, which undergo heat and chemical treatments, extra virgin olive oil is cold-pressed, preserving its natural properties. Choosing a lower-quality olive oil may result in fewer health benefits, as many of the important nutrients, such as monounsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols, can be lost during processing.
When selecting olive oil, pay attention to labels that indicate its origin and harvest date. High-quality extra virgin olive oil should be fresh, ideally used within 12 months of production to retain its beneficial properties. Choosing the right olive oil ensures that you maximize its health benefits, including its anti-inflammatory properties, heart-protective effects, and rich antioxidant content, making it a valuable addition to your diet. Ensure the farm is organic and that no chemical fertilizers or pesticides were used to treat the olives. Since blending extra virgin olive oil with non-extra virgin olive oil has become so prominent, it is important to make sure your olive oil comes from a "single estate" or "single origin". Sound like a lot? We've made it easy for you withour signature organic extra virgin olive oil.